Sodium humate and potassium humate are two common organic fertilizers, both based on humic acid, yet they exhibit significant differences. In this article, we will explore the distinctions between sodium humate and potassium humate to provide a better understanding of their applications in agriculture and soil improvement.

First and foremost, let’s discuss sodium humate. Sodium humate is a salt formed by the combination of humic acid with sodium ions (Na+), typically found in powdered or granular form. It is widely used in agriculture as an organic fertilizer primarily because of its ability to improve soil structure, enhance soil water retention, and increase soil fertility. Sodium humate can also neutralize soil acidity, making the soil more neutral and conducive to nutrient absorption by plants. Additionally, the sodium ions present in sodium humate can provide some essential nutrients to plants. However, it’s essential to note that excessive use of sodium humate can elevate the sodium content in the soil, which may have adverse effects on certain plants and soil types.

In contrast to sodium humate, potassium humate is a salt formed by the combination of humic acid with potassium ions (K+). Potassium humate can also be utilized as an organic fertilizer, but it offers distinct advantages in soil improvement. Firstly, potassium humate provides soluble potassium to plants, which is crucial for their growth and development. Potassium is one of the primary essential nutrients for plants, participating in various biochemical processes, such as cell division, water balance, and nutrient uptake. Therefore, the use of potassium humate aids in better nutrient absorption, resulting in improved yield and quality.

Furthermore, potassium humate can improve soil structure, increase soil permeability, and promote root growth. It also helps mitigate salt stress in soil because potassium can compete with sodium ions in the soil, reducing sodium accumulation in the soil. This is particularly beneficial for crops grown in saline soils.

Although both sodium humate and potassium humate have their merits in soil improvement and plant growth, there are notable differences between them. The primary nutrients they provide differ significantly, with sodium humate primarily supplying sodium and potassium humate mainly supplying potassium. Therefore, the choice of fertilizer should take into account the nutrient requirements of the plants and the specific soil conditions.
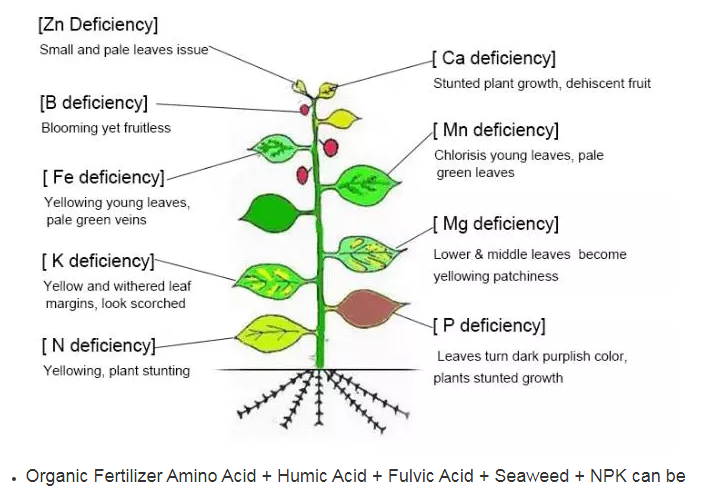
Secondly, sodium humate may be more favorable in acidic soils since it can neutralize soil acidity. Conversely, potassium humate is better suited for alkaline soils or situations where additional potassium fertilization is needed.
Moreover, sodium humate might increase the sodium content in the soil to some extent, which can have adverse effects on certain plants and soil types. Therefore, caution should be exercised when using sodium humate, especially in saline-alkali soils. In contrast, potassium humate helps alleviate soil salinity issues, making it more suitable for soil improvement in saline-alkali conditions.

Finally, cost is also a factor to consider when choosing between these fertilizers. Generally, the prices of sodium humate and potassium humate may vary, depending on production and market supply conditions.
In conclusion, sodium humate and potassium humate are two different types of organic fertilizers, each primarily composed of sodium and potassium ions, respectively. They offer distinct advantages and suitability for various applications based on the nutrient requirements of plants and the characteristics of the soil. When selecting a fertilizer, it’s crucial to consider the specific needs of your plants and the properties of the soil in which they will be grown.



 Facebook
Facebook Twitter
Twitter LinkedIn
LinkedIn Instagram
Instagram tiktop
tiktop